Sjfw
Release status: working
| Description | Firmware for Atmega644p and greater processors.
|
| License | GNU GPL v3
|
| Author | |
| Contributors | |
| Based-on | [[]]
|
| Categories | Firmware
|
| CAD Models | |
| External Link |
SJFW is a firmware for use with 3d printers. It has been tested on RAMPS and Gen4, but should be capable of supporting any modern RepRap motherboard.
Contents
- 1 Features
- 2 Media
- 3 Minimums and Requirements
- 4 Installing the Firmware
- 5 Current Issues and Notes
- 6 Printing with Compatible Host Software
- 7 Software Setup
- 8 Using Special Features
- 9 Customizing Hardware for Additional Features
- 10 Special Thanks
Features
- Bluetooth
- Control Panel
- LCD Display
- Hostless printing from SDcard.
- Full Runtime Configuration
- Temperature history graph
- Advanced Gcode Pipeline
- ISR driven movement
- Acceleration
- Works well with Pronterface Reprap host
- Supports ReplicatorG 3d Printing host
- Easy binary install
- Support for Thing-O-Matic / Gen4 with Extruder Controller
Media
These videos are outdated almost as soon as they are uploaded!
There are typically photos of recent development on the author's flickr page:
Minimums and Requirements
Hardware Minimums
- An Atmel Atmega 1280 or 2560 (644p support coming soon) based 3d printing motherboard
- Your hotend must be either using a 100k thermistor, or a Gen4/3 style extruder controller.
- Stepper-based extruder, no DC motors.
Software Minimums
- ReplicatorG to load the firmware and print
Recommended
- Pronterface host software.
Installing the Firmware
Method 1: Source Code Distribution
This is the "usual" way of configuring and installing a firmware on a Reprap. It's also only for the technically-savvy types, so if you're going to try it, you should already know what to do. In general, we recommend using ReplicatorG to load the generic firmware, under Method 2.
https://github.com/ScribbleJ/sjfw
Method 2: Load the Binaries
If you use the precompiled binaries, YOU MUST CONFIGURE YOUR PRINTER USING GCODE AT BOOT. You can find sample configurations here:
You can either add the configuration to your start.gcode at the /very/ beginning, or you can put it on an sdcard with the name 'sjfwauto.gcd' and it will be run at boot automatically every time your printer starts up. I STRONGLY RECOMMEND THE LATTER METHOD.
Using ReplicatorG (recommended method)
To install the firmware using ReplicatorG, start by downloading and installing the latest version of ReplicatorG for your operating system:
Run it, open the File menu, and choose Preferences. In the "Firmware update URL" put the following: http://scribblej.com/firmware.xml
Close the window to save your changes, then open the "Machine" menu and choose "Upload new firmware."
You should see the following choices:
- Arduino Mega1280 with EC (ToM)
- Arduino Mega2560 with EC (ToM)
- Arduino Mega1280 with 100k therm (RAMPS13)
- Arduino Mega2560 with 100k therm (RAMPS13)
Choose the one that is appropriate for your machine, and follow the prompts from there. If there is no option appropriate for you, then you must fall back on Method 1. The machines in parentheses are the provided configuration files, but if you want to set up your own configuration, they will work for any board with the proper temperature control and Atmega chip. If you do create a custom configuration, please contribute it for inclusion in sjfw! See the Software Setup section for details.
While RepG is uploading the firmware, it doesn't give any feedback, unless you are looking at the terminal you launched it from. It should take about 1 minute to upload the firmware.
If RepG Fails
RepG can fail for any number of reasons. If it happens to you, it sucks. Here's a few things to try short of abandoning sjfw or resorting to method 1.
1) On some operating systems, ReplicatorG will output extra information to a terminal window, if it's started from the command line.
2) ReplicatorG preferences include an option to show you more logging information, turning this to ALL may show something interesting.
3) ReplicatorG and the Arduino environment both include a copy of avrdude to burn firmwares. You can attempt running it directly from the commandline. If you are using ReplicatorG, use the commandline to navigate to the tools directory, and make sure you've put a copy of the firmware binary you want in the same directory. Then try something like:
For 1280:
avrdude.exe -C avrdude.conf -D -P COM3 -b 57600 -p m1280 -V -c stk500v1 -U flash:w:1280-w-100k-v1.0.hex:i
For 2560:
avrdude.exe -C avrdude.conf -D -P COM3 -b 115200 -p m2560 -V -c stk500v2 -U flash:w:2560-w-100k-v1.0.hex:i
If you STILL have problems, PLEASE let the developer know!
VERY, VERY, VERY IMPORTANT!
YOU MUST RUN THE GCODE TO INITIALIZE YOUR PRINTER AFTER EVERY TIME IT IS RESTARTED!
You have TWO good options:
1) The SIMPLE, RELIABLE, and RECOMMENDED WAY: Put the configuration gcode in a file named 'sjfwauto.gcd' on your sdcard and leave it in there every time you boot up.
2) The OTHER WAY: Put the configuration gcode at the very start of your start.gcode file. You may want to keep it around as a file you can run before you try the control panel in your host, too, because you'll need to do that.
Current Issues and Notes
IMPORTANT THINGS
- This firmware is only heavily tested by the author, so far. Please help if you are daring, but it's important to note that the firmware comes with no promises or guarantees, and if it burns your house down or eats your babies, the author will not be held responsible.
- If you use the binary distribution, YOU MUST execute configuration gcode before printing!
- There is no homing command. There probably never will be; it's unnecessary. Just make a move towards the endstops that is longer than the platform, then mark that spot with a G92 and carry on. Here's some examples:
Prusa start.gcode
M104 S190 (start heating up, but don't wait) G92 X0 Y0 Z0 E0 (set current position) G1 X-300 Y-300 F2000 (Move to X/Y endstops) G92 X0 Y0 Z0 E0 (set current position) G1 X5 Y5 (Move away from X/Y endstops) G92 X0 Y0 Z0 E0 (set current position) G1 X-10 Y-10 F800 (Move back to X/Y endstops) G1 Z-200 F400 (Move to Z endstop) G92 X0 Y0 Z0 E0 (set current position) G1 Z5 F400 (Move away from Z endstop) G92 X0 Y0 Z0 E0 (set current position) G1 Z-10 F400 (Move to Z endstop) G92 X0 Y0 Z-0.7 E0 (set current position - note endstop is .7 below platform height) G1 X0 Y0 Z30 F2000 (move to waiting position) M109 S190 (wait for extruder to reach temperature)
Thing o Matic start.gcode
M104 S180 (start heating extruder, but don't wait) M140 S50 (start heating platform, but don't wait) G92 X0 Y0 Z0 E0 (set current position) G1 Z200 F800 (move to Z endstop) G1 X-200 Y-200 F2000 (move to X,Y endstops) G92 X0 Y0 Z0 E0 (set current position) G1 Z-5 X5 Y5 F800 (move away from XYZ endstops) G92 X0 Y0 Z0 E0 (set current positions) G1 Z10 X-10 Y-10 F400 (move to XYZ endstops) G92 X-5 Y-25 Z116.7 E0 (set current positions) G1 X0 Y0 Z50 F6000 (move to waiting position) M84 (disable motors) M109 S180 (wait for extruder to reach temperature)
MINOR THINGS
- Config file for ramps13 includes everything; the others may need some love for control panel and lcd support.
- Gen4 EC support assumes you are running the standard Makerbot EC firmware on your Extruder Controller.
- Motors that are set to disable after a move only get disabled a few moves thereafter. This should work fine, but don't forget a M84 at the end of your gcode to turn off all motors.
- SD card support works in the firmware, but is not compatible with the Gcodes that Pronterface and ReplicatorG emit for SDcard access. This firmware presently has two Gcodes for SD access:
- M204 - fetch filename from SD
- M205 - print last fetched filename
- The 4-bit LCD display mode does not always initialize properly from poweron due to timing issues. If your LCD looks garbled, reset the motherboard while leaving the power to the LCD on, sometimes twice in a row. You can just hit the 'reset' button on the motherboard. It'll be fine foreverafter, 'till you power down.
- The SD code may only work properly for 8.3 filenames.
Printing with Compatible Host Software
sjfw has been tested to work with the following hosts, with varying levels of compatibility:
Printing with Pronterface (Recommended)
You can get it here:
https://github.com/kliment/Printrun
Pronterface should work right out of the box with sjfw. You will need to change the serial baudrate from the Pronterface default of 115200, to the sjfw value of 57600.
Pronterface's SD card buttons will not work with sjfw. You can initiate an SD card print manually using Pronterface's gcode input box. Just send M204 until you see the file you want to print, then M205.
Printing with ReplicatorG
You can get it here:
ReplicatorG requires modifying its configuration file to speak to sjfw. You need to edit machines/reprap.xml and add the following:
<machine experimental="0">
<name>sjfw</name>
<geometry type="cartesian">
<axis id="x" length="200" maxfeedrate="12000" stepspermm="1" endstops="min"/>
<axis id="y" length="200" maxfeedrate="12000" stepspermm="1" endstops="min"/>
<axis id="z" length="150" maxfeedrate="400" stepspermm="1" endstops="min"/>
</geometry>
<tools>
<tool name="Stepper-based extruder" type="extruder" material="abs" motor="true" floodcoolant="false" mistcoolant="false" fan="true" valve="false" collet="false" heater="true" stepper_axis="a" motor_steps="1" heatedplatform="true" />
</tools>
<clamps></clamps>
<firmware url="???" autoupgrade="false"></firmware>
<help name="Sjfw Help" url="http://reprap.org/wiki/Sjfw"></help>
<driver name="reprap5d">
<okAfterResend>false</okAfterResend>
<pulserts>false</pulserts>
<waitforstart enabled="false"></waitforstart>
<debugLevel>0</debugLevel>
<fived>true</fived>
<rate>57600</rate>
</driver>
<warmup>
</warmup>
<cooldown>
</cooldown>
</machine>
After this, you should be able to select 'sjfw' in the Machine->Drivers menu in ReplicatorG, and use it as normal. ReplicatorG has extensive documentation around the internet.
Presently, RepG does not report the correct bed temperature from sjfw. It may have other issues, as well.
sjfw perl host
This was mainly written as a test bed, but is perfectly useable for printing if you have perl and the Device::SerialPort perl library installed. This should be available for all operating systems. In addition, the sjfw perl host is the only host presently to support advanced CRC calculations. The advanced CRC is disabled in the precompiled binary (and by default in host.pl) so if you'd like to try advanced CRC, you'll need to compile your own.
Advanced CRC
Advanced CRC solves the problem inherent in the Reprap CRC algorithm; a gcode like 'G1 X10 Y10 Z10 F1000" can drop half it's characters and STILL be interpreted as valid using the normal Reprap CRC. If you ever have comms errors (who doesn't?) this can cause your head to spontaneously shoot a vast distance across the platform for no apparent reason, screwing your print for good. The Advanced SJFW CRC is not bulletproof, but is a simple change and vast improvement over the Reprap CRC.
Advanced CRC support has also been coded for ReplicatorG but is not in the current release.
Software Setup
There is example gcode in the distribution for use with the precompiled firmware; look in the generic folder to see examples of the Gcode required to configure your printer. The full syntax is documented below, as well. If you create a custom configuration for your printer, please contribute it to sjfw with a push request, or email it to [email protected].
The precompiled hex files are as generic as possible, but have the SD select pin pre-defined so that you can have the configuration of your particular printer load from SD at boot. If you do not have an SD, no worries, you can still use them, but you'll need to add the configuration code to your start.gcode so it is properly configured before attempting to print.
When using the LCD and Keypad in the generic firmwares, they are hard-coded to expect a 16button pad and 20x4 LCD presently. If you do not have either one, that is fine, but if you do, they must be of that size, or you must compile your own firmware instead of using the precompiled.
Runtime Configuration Gcodes
NOTE: This system of commands is not ideal, but it was quick to implement. It may change later to be more user-friendly and consistent.
sjfw introduces some new gcodes and new usage of gcodes for its own configuration. There is absolutely no intention to have these commands adopted by the community as they are presently.
Steps and Speed settings
- M200 - accepts XYZE parameters. Set steps per mm.
- M201 - accepts XYZE parameters. Set start speed in mm/min.
- M202 - accepts XYZE parameters. Set maximum speed in mm/min.
- M203 - accepts XYZE parameters. Set 'average' speed in mm/min. Currently, this can be ignored; it is not used.
NOTE! To avoid any possible issues, always send all four of the commands above together, and always set the steps per mm before the feedrates.
- M206 - accepts XYZE parameters. Set acceleration in mm/s/s.
Heating Elements Pin Settings
- M207 - accepts P and S parameters.
- P = Set hotend thermistor analog pin, using analog pin number. -1 to disable.
- S = Set hotend FET output pin, USING ARDUINO PIN NUMBERING.
- M208 - accepts P and S parameters
- P = Set platform thermistor analog pin, using analog pin number. -1 to disable.
- S = Set platform FET output pin, USING ARDUINO PIN NUMBERING.
Axis Pin Settings
NOTE: THE BINARY INSTALL v1.0 DOES NOT SUPPORT THESE SETTINGS. AN UPDATE WILL BE OUT SHORTLY.
- M309 - accepts P and S parameters - THIS MUST HAPPEN BEFORE YOU CALL M304/M305 OR ELSE!
- P1 for endstops inverted
- S1 for endstop pullups
- M300 - accepts XYZE parameters - Set axis STEP pins USING ARDUINO PIN NUMBERS
- M301 - accepts XYZE parameters - Set axis DIR pins USING ARDUINO PIN NUMBERS
- M302 - accepts XYZE parameters - Set axis ENABLE pins USING ARDUINO PIN NUMBERS
- M304 - accepts XYZE parameters - Set axis MIN pins USING ARDUINO PIN NUMBERS
- M305 - accepts XYZE parameters - Set axis MAX pins USING ARDUINO PIN NUMBERS
- M307 - accepts XYZE parameters - Set axis inversion, 1=inverted, 0=not
- M308 - accepts XYZE parameters - Set axis disable after move, 1=disable, 0=not
- M310 - accepts no parameters - outputs a list of unset pins for all axis, as well as the value of the inversion, disable, and endstop flags
Random Sjfw-Specific Gcode
- M211 - accepts P parameter - P parameter sets number of milliseconds between automatic temperature reports. VALUES < 2000 NOT RECOMMENDED.
- M204 - no parameters - display next SD card filename.
- M205 - no parameters - print file last displayed by 204.
"Special" Configuration Gcode
This section will be gone completely as soon as alternative methods for setting the LCD and Keypad pins are provided.
In addition to the above codes, there is a special format for setting pins on all subsystems (except SD card). To begin, you send the code M1 G1 as a single line of gcode, which in other circumstances would be illegal. Then you can add as much pin configuration to the line as you like.
Configuration strings are formatted beginning with a subsystem selector, and from there, configuration options in an arcane format described here:
SUBSYSTEMS:
- '^' - LCD Subsystem
- '&' - Keypad Subsystem
AXIS Subsystem config
The general format following the '$' specifier is a letter of an axis (note the extruder is 'A' here, NOT 'E') followed by a series of settings for that axis.
The following example contains all the axis-specific commands:
M1 G1 $XSF0DF1ED7IE5A--N0X0
It is possible to break this command down into its parts on separate lines, for readability:
M1 G1 $XSF0 (Set 'X' axis 'S' Step pin to port F, pin 7) M1 G1 $XDF1 (Set 'X' axis 'D' Dir pin to port F, pin 1) M1 G1 $XED7 (Set 'X' axis 'E' Enable pin to port D, pin 7) M1 G1 $XIE5 (Set 'X' axis 'I' mIn endstop pin to port E, pin 5) M1 G1 $XA-- (Set 'X' axis 'A' mAx endstop to disabled/unused) M1 G1 $XN0 (Set 'X' axis 'N' iNvert to '0' = false) M1 G1 $XX0 (Set 'X' axis 'X' disable to '0' = false)
In addition, there are two commands that must include an axis specifier, but take effect globally.
M1 G1 $XJ1K1
- J(1 or 0) Enable/disable Endstop Pullups
- K(1 or 0) Enable/disable Endstop Inversion
PLEASE NOTE, YOU MUST SET THE J/K OPTIONS BEFORE YOU SET ANY AXIS ENDSTOP PINS, OR RE-SET THE ENDSTOP PINS AFTER CHANGING VALUES.
Temperature Subsystem
This subsystem currently only has two options. Here they are by example:
M1 G1 %HB4 (Set 'H'otend FET pin to Port B,4) M1 G1 %BH5 (Set 'B'ed FET pin to Port H,5)
LCD Subsystem
Here are the options by example:
G1 M1 ^SK1 (Set LCD RS to Port K,7) G1 M1 ^WL7 (Set LCD RW ...) G1 M1 ^EK3 (Set LCD Enable) G1 M1 ^4F5 (Set LCD D4) G1 M1 ^5K2 (Set LCD D5) G1 M1 ^6L5 (Set LCD D6) G1 M1 ^7K4 (Set LCD D7 - always set D7 last, LCD activates automatically when D7 is set.)
Keypad Subsystem
G1 M1 &R0H1 (Set Keypad Row0 to Port H,1) G1 M1 &R1H0 (Set Keypad Row1) G1 M1 &R2A1 (Set Keypad Row2) G1 M1 &R3A3 (Set Keypad Row3) G1 M1 &C1A7 (Set Keypad Col1) G1 M1 &C2C6 (Set Keypad Col2) G1 M1 &C3C4 (Set Keypad Col3) G1 M1 &C0A5 (Set Keypad Col0 - always set last, is flag for activation)
Subsystem Common Example
If you prefer, you may set multiple commands on one line:
G1 M1 ^SK1WL7EK34F55K26L57K4 &R0H1R1H0R2A1R3A3 &C1A7C2C6C3C4C0A5
Keep in mind sjfw currently presents a 'fragment' maximum size of 32 - the distance between spaces in the gcode line.
Using Special Features
Bluetooth
The bluetooth support is new, and needs new documentation to match.
Printing from bluetooth works just fine, but my real hope is that someone will use the support for something truly interesting, like an Android/iPad printer control panel, or even just a really nice wired-up control panel that is smart enough to speak gcode. Anything you can plug in to the port that speaks 9600 baud serial will work, so it's not really limited to Bluetooth.
You can have a USB host and a 'bluetooth' host connected at the same time without interference, so it is possible to use this feature to design a truly advanced control panel.
SD Card
PLEASE NOTE: GCode on the sdcard must be 'raw' gcode! No comments in the file, please!
PLEASE NOTE: Filenames must be 8.3
- M204 - display next filename.
- M205 - execute the last file displayed by M204.
SD Card Autorun
sjfw includes an option to look for a specially-named file on the sd card and run it at boot. This is especially useful to automatically configure the generic firmwares at boot; just put your configuration gcode in the magic file and it will always run first thing.
The magic filename is 'sjfwauto.gcd'
If you are connected with a host at boot, you will see output before the 'start' is sent by the printer, showing whether the sjfwauto.gcd has been/is being executed, or if it failed to read the file.
LCD and Keypad
Currently, the LCD system consists of 3 screens. You can switch between them anytime using the 'A','B','C' buttons on your pad.
Temperature Display/Control
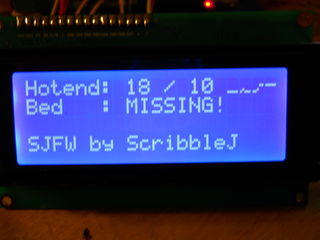 This is the default screen and is selected with 'A'.
This is the default screen and is selected with 'A'.
The upper right includes a temperature history graph. The center of the graph is always the currently-set temperature.
Keypad controls for this screen:
- 1 = Raise hotend setpoint by 5deg.
- 4 = 0 hotend setpoint
- 7 = Lower hotend setpoint by 5deg.
- 3 = Raise platform setpoint by 5deg.
- 6 = 0 platform setpoint
- 9 = Lower platform setpoint by 5deg.
SD Card Printing
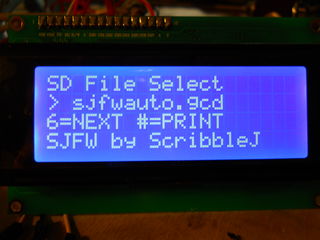 When an SD print is in progress, this screen will change to simply display it's filename.
When an SD print is in progress, this screen will change to simply display it's filename.
Keypad controls for this screen:
- '6' = Next file.
- '#' = Print.
Position/Motor Control
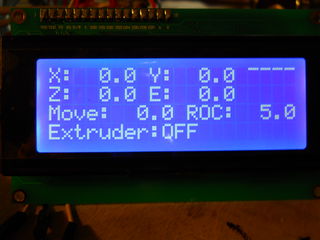 This screen is a bit complicated! Here's what it's showing:
This screen is a bit complicated! Here's what it's showing:
- XYZE = current motor position (at end of parsed gcode, so may not be /current/)
- Upper Right = Temperature history graph.
- Move: When you click an axis move button, it will move this far.
- ROC: When you click the Move Increment/Decrement buttons, the "Move" values changes by this amount.
- Extruder: This /does not monitor the current extruder status/ it simply shows you whether the extruder will run when you move an axis using the pad.
And here are the keypad controls for this screen:
- 1/7 = Move increment/decrement
- '*' = Toggle extruder
- '#' = Next ROC
- '5' = Disable all motors.
- 2/8 = Move Y
- 4/6 = Move X
- 3/9 = Move Z
Customizing Hardware for Additional Features
At a minimum, you must have (LCD)7 + (KEYPAD)8 = (TOTAL)15 free pins on your motherboard to use the precompiled binary control panel support.
You can use just the LCD for temperature display without attaching a keypad, if you'd like to save pins. Or you can wait for other options to be included.
Below are examples on this for RAMPS 1.3; for other hardware, though this doesn't directly apply, it should help guide you in determining where to put things.
Connecting an LCD to RAMPS 1.3
The provided configuration assumes you will connect the LCD in 4-bit mode to AUX2.
- D63 = RS
- D42 = RW
- D65 = E
- D59 = Data4
- D64 = Data5
- D44 = Data6
- D66 = Data7
The Data0 - Data3 pins on the LCD are left disconnected. The contrast pin on the LCD can be wired to ground, or run through a pot between ground and +5v for adjustable contrast.
There are plans to add i2c support to sjfw as soon as I have an i2c LCD and/or keypad with which to test code. In the meantime, SJFW supports hitachi-protocol text-mode LCDs using a parallel interface. These are as common as dirt; basically any 16x2 or 20x4 character display with 16 pins is going to be the right thing. I recommend 20x4, but the firmware supports both sizes. It /does not/ support single-line displays. If you'd like that support, a patch would be simple.
WHY IS D48 THE UNUSED PIN ABOVE WHEN D65 WOULD MAKE MORE SENSE? Simply because D48 is burned out on my RAMPS board.
WHY CONNECT RW? SJFW uses RW to poll the LCD's busy state for fast, fast, fast access. It is required.
Connecting a keypad to RAMPS 1.3
 (Use pins shown in photo below, NOT these)
(Use pins shown in photo below, NOT these)
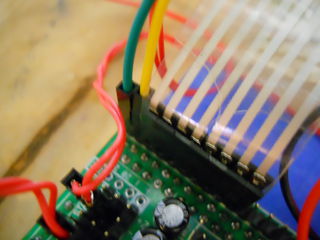 Shown here with Bluetooth connection as well.
Shown here with Bluetooth connection as well.
The provided configuration assumes you will connect a 16-button keypad using 8 pins of AUX-4.
- D23 = ROW1
- D25 = ROW2
- D27 = ROW3
- D29 = ROW4
- D31 = COL1
- D33 = COL2
- D35 = COL3
- D37 = COL4
The top two pins, D16 and D17, are unusued for the pad because they expose a com port that can be used for Bluetooth or other backup serial comms.
Keypads are supported using a row/column scanning method. This is a very common style of keypad, and also easy to make yourself. You should expect to see 8 pins for a 4x4 button pad grid. If you have a datasheet, the pins will be labeled COLUMN1-4 and ROW1-4. While it is easy to change SJFW to support 9-button pads or any random number of buttons, currently the code rather assumes you have 16.
Connecting Bluetooth or other Serial Device to RAMPS 1.3
 Bluetooth support is not presently included in the binary distribution, you must compile your own to access this functionality.
Bluetooth support is not presently included in the binary distribution, you must compile your own to access this functionality.
- D16 = RXD
- D17 = TXD
Any 5-volt Bluetooth dongle should do. The one in the photo is available for < $15 at mdfly.com. When I added this to my RAMPS13 it caused power fluctuations that made the thermistors readings go out of whack. I solved it by switching the power pins for the dongle to a separate power rail, however they MUST share a common ground or the dongle may not register the TXD/RXD signals properly.
The serial connection here is set to 9600. This is PLENTY FAST for sjfw, with the advanced gcode pipeline you can go almost arbitrarily slow on comms and still have a fast print.
Any device that can speak gcode at the printer over 9600 serial can be connected here. It is not limited to Bluetooth.
Special Thanks
- EVERYONE on #reprap on irc.freenode.net -- I could not have done it without your knowledge.