Selective laser sintering
Revision as of 14:19, 11 September 2018 by John Cummings (talk | contribs)
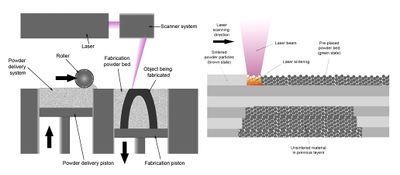
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing (AM) technique that uses a laser as the power source to sinter powdered material, aiming the laser automatically at points in space defined by a 3D model, binding the material together to create a solid structure. Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) is a form of SLS used to create metal objects.
Components
- Build chamber: The chamber around the SLS system used to keep the area heated and to stop laser light escaping
- Heaters: heats the build chamber to just below the temperature needed to fuse the powder
- Powder delivery system: provides powder to the printer
- Recoater: adds layers of powder on top of the model to be fused
- Laser: fuses the printing medium together, the heated build chamber allows the use of a lower powered laser
- X-Y scanning mirror: directs the laser light to the correct place
- Build platform: The platorm which objects attach to as they are built
- Overflow bin: stores excess print powder which is produced as each new layer of powder is added before the laser sinters the layer.