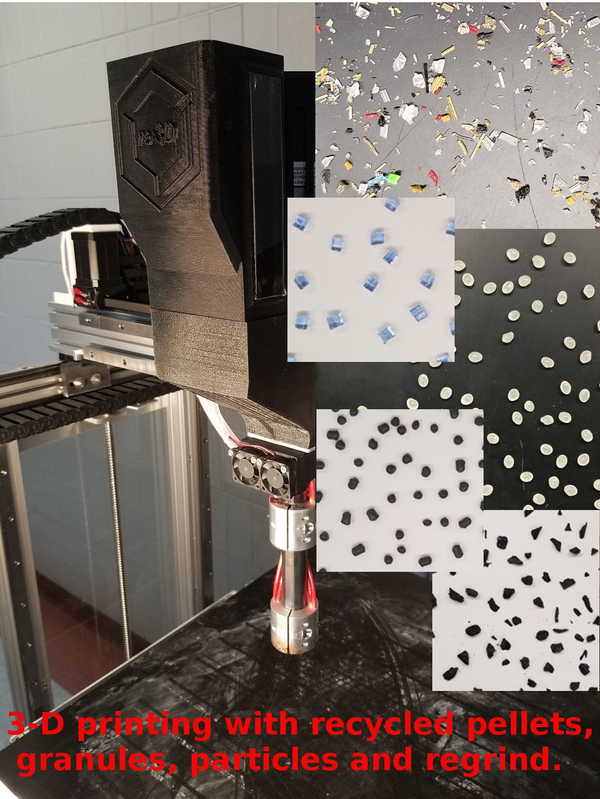
Fused Particle Fabrication 3-D Printing: Recycled Materials’ Optimization and Mechanical Properties

|
By Michigan Tech's Open Sustainability Technology Lab.
Wanted: Students to make a distributed future with solar-powered open-source RepRap 3-D printing and recyclebot recycling. |

|
Source
- Woern, A.L.; Byard, D.J.; Oakley, R.B.; Fiedler, M.J.; Snabes, S.L.; Pearce, J.M. Fused Particle Fabrication 3-D Printing: Recycled Materials’ Optimization and Mechanical Properties. Materials 2018, 11, 1413. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081413 open access
- Just the code: https://osf.io/fsjk9/
- https://re3d.org/
Abstract
Fused particle fabrication (FPF) (or fused granular fabrication (FGF)) has potential for increasing recycled polymers in 3-D printing. Here, the open source Gigabot X is used to develop a new method to optimize FPF/FGF for recycled materials. Virgin polylactic acid (PLA) pellets and prints were analyzed and were then compared to four recycled polymers including the two most popular printing materials (PLA and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)) as well as the two most common waste plastics (polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP)). The size characteristics of the various materials were quantified using digital image processing. Then, power and nozzle velocity matrices were used to optimize the print speed, and a print test was used to maximize the output for a two-temperature stage extruder for a given polymer feedstock. ASTM type 4 tensile tests were used to determine the mechanical properties of each plastic when they were printed with a particle drive extruder system and were compared with filament printing. The results showed that the Gigabot X can print materials 6.5× to 13× faster than conventional printers depending on the material, with no significant reduction in the mechanical properties. It was concluded that the Gigabot X and similar FPF/FGF printers can utilize a wide range of recycled polymer materials with minimal post processing.Keywords
Circular economy; Distributed recycling; Energy conservation; Polymer recycling; Sustainable development; distributed manufacturing; life cycle analysis; recycling; recyclebot; 3-D printing; Open source hardware; Open hardware; RepRap; Recycling; Polymers; Plastic; Recyclebot; Waste plastic; Composites; Polymer composites; Extruder; Upcycle; Materials science;additive manufacturing; distributed manufacturing; open-source; waste plastic; extruder; upcycle
See Also
- Recyclebot
- 3-D Printable Polymer Pelletizer Chopper for Fused Granular Fabrication-Based Additive Manufacturing
- Tightening the loop on the circular economy: Coupled distributed recycling and manufacturing with recyclebot and RepRap 3-D printing
- Energy Payback Time of a Solar Photovoltaic Powered Waste Plastic Recyclebot System
- Wood Furniture Waste-Based Recycled 3-D Printing Filament
- Life cycle analysis of distributed recycling of post-consumer high density polyethylene for 3-D printing filament
- Evaluation of Potential Fair Trade Standards for an Ethical 3-D Printing Filament
- Mechanical Properties of Components Fabricated with Open-Source 3-D Printers Under Realistic Environmental Conditions
- Mechanical testing of polymer components made with the RepRap 3-D printer
- Development and feasibility of applications for the RepRap 3-D printer
- Life cycle analysis of distributed polymer recycling
- Solar powered distributed customized manufacturing
- Distributed recycling of post-consumer plastic waste in rural areas
- Ethical Filament Foundation
- Economist article on U. of Washington's HDPE boat, Oprn3dp.me
- Cruz, F., Lanza, S., Boudaoud, H., Hoppe, S., & Camargo, M. Polymer Recycling and Additive Manufacturing in an Open Source context: Optimization of processes and methods. http://sffsymposium.engr.utexas.edu/sites/default/files/2015/2015-127-Cruz.pdf
- https://ultimaker.com/en/resources/52444-ocean-plastic-community-project
Literature Reviews
- Waste plastic extruder: literature review
- Life cycle analysis of polymer recycling literature review
In the news
- Optimizing the Properties of Recycled 3D Printing Materials 3D Print 40.1k
- re: 3D GIgabot X ottimizzazione delle proprietà dei materiali di stampa 3D riciclati Stampare in 3D
- Gigabot X: Optimierung von recycelten Filamenten 3DRuck